I’ve spent years diving deep into the world of short fiction, and I can tell you that studying exceptional short story examples is one of the fastest ways to elevate your writing. Whether you’re a budding writer looking to understand what makes stories tick or an educator seeking powerful teaching tools, these 25 masterpieces will give you everything you need.
What makes these particular short story examples so special? Each one demonstrates specific techniques that you can learn and apply to your own work. From Hemingway’s iceberg theory to Carver’s minimalism, these stories showcase the full spectrum of what’s possible in short fiction.
I’ve organized this guide to help you understand not just what these stories are about, but why they work so brilliantly. You’ll discover how to evaluate short story quality, learn specific techniques from each example, and understand how these lessons apply to modern writing challenges.
What Makes a Short Story Example Worth Studying

Source: researchgate.net
When I evaluate short story examples for teaching or inspiration, I look for works that demonstrate masterful craft through precise language, compelling characters, and seamless theme integration. The best examples offer clear learning opportunities while maintaining contemporary relevance across different audiences.
Literary quality assessment focuses on narrative structure, character development, language precision, and thematic sophistication. These elements work together to create stories that resonate long after you’ve finished reading them. A truly exceptional short story makes every word count, develops characters efficiently, and integrates themes naturally into the narrative flow.
Educational value evaluation includes technical demonstration, genre representation, accessibility levels, and cultural relevance for diverse learning contexts. The most valuable short story examples teach specific techniques while remaining engaging enough to hold reader interest. They should demonstrate clear writing principles that emerging writers can identify and practice in their own work.
Writers seeking to expand their understanding of narrative techniques can explore unconventional storytelling approaches that challenge traditional boundaries while maintaining the fundamental excellence demonstrated in these classic works.
Essential Criteria for Evaluating Short Story Quality
Effective short story evaluation requires examining four core areas that determine lasting impact and educational value. Literary craft encompasses narrative structure, character development, language style, and theme integration – the technical foundation that separates professional work from amateur attempts.
Educational potential includes technical demonstration of writing techniques, clear genre representation, appropriate accessibility, and cultural significance. The best teaching stories show rather than tell how specific techniques work, making abstract concepts concrete through practical application.
Practical considerations involve length appropriateness, audience suitability, teaching potential, and inspiration factor for creative development. A story might be technically brilliant but too complex for its intended audience, or perfectly accessible but lacking the depth needed for serious study.
| Evaluation Criteria | Weight | Key Indicators | Assessment Questions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Literary Craft | 40% | Narrative structure, character depth, language precision, thematic integration | Does the story demonstrate technical mastery? Are characters fully realized? |
| Educational Value | 25% | Teaching potential, technique demonstration, accessibility, cultural significance | What specific skills can students learn? Is it appropriate for target audience? |
| Contemporary Relevance | 20% | Modern themes, current issues, timeless appeal, cultural diversity | Does it speak to today’s readers? Does it represent diverse perspectives? |
| Practical Application | 15% | Length appropriateness, classroom utility, inspiration factor, discussion potential | Can it be effectively taught? Will it motivate student writers? |
1. “The Lottery” by Shirley Jackson

Source: freepik.com
Jackson’s masterpiece follows a seemingly peaceful village conducting their annual lottery, building tension through ordinary details before revealing the shocking violent conclusion. This short story demonstrates perfect dramatic irony as readers gradually understand what villagers already know.
The work excels in social commentary about tradition, conformity, and humanity’s capacity for violence while maintaining accessible prose that masks its sophisticated themes. Jackson’s masterful use of dramatic irony and misdirection through seemingly innocent village descriptions becomes sinister upon revelation.
Her powerful social commentary examines blind adherence to tradition versus individual moral responsibility in community settings. The story forces readers to question their own participation in harmful social practices.
Dramatic Irony Technique Analysis: Jackson opens with “The morning of June 27th was clear and sunny, with the fresh warmth of a full-summer day; the flowers were blossoming profusely and the grass was richly green.” This pastoral description creates false security, making the violent conclusion more shocking. Writers can apply this technique by establishing normal, pleasant settings before introducing conflict, creating powerful emotional contrast that enhances story impact.
2. “A Good Man Is Hard to Find” by Flannery O’Connor
O’Connor’s Southern Gothic tale follows a family road trip that turns deadly when they encounter an escaped convict called The Misfit. The short story operates on multiple levels – surface narrative, family dysfunction study, and spiritual allegory.
O’Connor’s grotesque realism creates simultaneously repulsive and sympathetic characters while exploring themes of grace, redemption, and moral blindness through the grandmother’s final moment of recognition. Her Southern Gothic style demonstrates grotesque realism and complex character development that reveals human nature’s contradictions.
The theological complexity explores grace and redemption themes through multi-layered narrative structure and symbolic character interactions. O’Connor forces readers to confront uncomfortable truths about human nature and divine grace.
3. “The Yellow Wallpaper” by Charlotte Perkins Gilman

Source: mayflowerwallpaper.com
Gilman’s pioneering feminist work chronicles a woman’s descent into madness during a “rest cure” for postpartum depression. The diary format creates intimacy while the unreliable narrator technique forces readers to question reality alongside the protagonist.
The wallpaper becomes a master symbol representing women’s confinement within patriarchal structures, functioning as both medical horror and feminist manifesto. Gilman’s innovative use of unreliable narrator technique combined with diary format creates psychological realism and reader immersion.
This groundbreaking feminist literature uses symbolic representation and medical horror elements to critique patriarchal oppression. The story remains powerfully relevant to contemporary discussions about women’s autonomy and medical treatment.
4. “Hills Like White Elephants” by Ernest Hemingway
Hemingway’s minimalist masterpiece presents a couple discussing an “operation” (implied abortion) while waiting for a train in Spain. The short story exemplifies the iceberg theory where 90% of meaning lies beneath surface dialogue.
Every word serves the story’s purpose, demonstrating how subtext and omission can create more powerful impact than explicit statement. The work remains relevant due to ongoing reproductive rights discussions.
Hemingway’s perfect demonstration of iceberg theory and minimalist prose shows how subtext carries primary narrative weight through dialogue technique. His masterful use of omission and implication creates emotional resonance while addressing controversial topics through indirect approach.
Subtext Through Dialogue Technique: Hemingway never explicitly mentions “abortion” but uses phrases like “It’s really an awfully simple operation” and “They just let the air in and then it’s all perfectly natural.” Writers can master this technique by having characters discuss sensitive topics through euphemisms and implications, allowing readers to understand the true subject while maintaining narrative subtlety and emotional power.
5. “The Tell-Tale Heart” by Edgar Allan Poe

Source: etsy.com
Poe’s psychological horror follows a narrator confessing to murdering an old man, driven mad by the victim’s “vulture eye.” The short story showcases unreliable narration, building tension, and atmospheric creation through first-person perspective.
Poe’s exploration of guilt, paranoia, and psychological deterioration established foundations for modern psychological horror while demonstrating how narrative voice can become the story’s primary source of terror. His pioneering use of first-person unreliable narrator creates psychological horror through voice and perspective manipulation.
The masterful tension building and atmospheric creation uses repetitive language patterns and escalating psychological pressure. Poe proves that the human mind can be more terrifying than any external monster.
6. “The Gift of the Magi” by O. Henry
O. Henry’s Christmas classic tells of a poor couple who sacrifice their most prized possessions to buy each other gifts. The short story demonstrates perfect situational irony and the twist ending that became O. Henry’s trademark.
Despite its simple surface, the work explores themes of sacrifice, love, and wisdom while showing how narrative economy can achieve maximum emotional impact in minimal space. The classic demonstration of situational irony and twist ending technique maximizes emotional payoff through delayed revelation.
O. Henry’s exploration of sacrifice and love themes through narrative economy achieves complete character arcs in minimal word count. The story proves that profound truths can emerge from simple situations.
7. “What We Talk About When We Talk About Love” by Raymond Carver
Carver’s minimalist short story presents two couples drinking and discussing love’s nature in a kitchen on Saturday afternoon. The work showcases naturalistic dialogue while maintaining thematic coherence through repetitive patterns that mirror actual speech.
Each character’s distinct voice emerges through word choice and rhythm variations, demonstrating how conversation can reveal relationship dynamics and emotional complexity. Carver’s minimalist prose technique uses naturalistic dialogue to explore complex relationship dynamics through subtext and implication.
His character voice development through distinct speech patterns and conversational rhythm reveals personality and emotional states. The story shows how ordinary conversations can expose extraordinary depths of human experience.
8. “The Things They Carried” by Tim O’Brien
O’Brien’s metafictional work follows soldiers in Vietnam carrying physical and emotional burdens during war. The short story blurs fiction and memoir while exploring memory, trauma, and storytelling’s power.
O’Brien’s technique of listing physical objects creates emotional weight while examining how material possessions connect to psychological states. The work demonstrates how war literature can transcend genre boundaries.
The innovative metafictional technique blurs memoir and fiction boundaries while exploring storytelling’s relationship to truth and memory. O’Brien’s symbolic use of physical objects represents emotional and psychological burdens through detailed cataloging and weight metaphors.
9. “Cathedral” by Raymond Carver
Carver’s short story follows a man whose prejudices are challenged when his wife’s blind friend visits their home. The intimate domestic setting facilitates character transformation as the confined space forces genuine interaction.
The cathedral drawing becomes shared creative space enabling mutual understanding, demonstrating how empathy develops through direct experience rather than abstract knowledge. The character transformation arc shows prejudice overcome through direct experience and shared creative activity.
Carver’s effective use of confined domestic setting forces character interaction and facilitates genuine human connection development. The story proves that understanding comes through experience, not explanation.
10. “Interpreter of Maladies” by Jhumpa Lahiri

Source: hikingartist.com
Lahiri’s short story features an Indian-American tour guide reflecting on cultural disconnection and marital problems. The work showcases cultural translation as both theme and technique through dual consciousness reflecting immigrant experience.
The interpreter’s job parallels characters’ attempts to decode their own emotional lives, demonstrating how professional roles can mirror personal struggles. Lahiri’s cultural identity exploration through dual consciousness technique reflects immigrant experience and cultural navigation challenges.
Her metaphorical framework where professional interpretation work parallels personal emotional decoding and relationship understanding creates layers of meaning. Understanding how modern writers craft compelling first-person narratives can illuminate Lahiri’s sophisticated use of perspective to explore cultural identity and emotional complexity.
11. “The Swimmer” by John Cheever
Cheever’s surreal tale follows a man attempting to swim home through neighbors’ pools, revealing suburban emptiness. The short story employs magical realism within suburban settings, creating surreal progression as Neddy’s journey becomes increasingly nightmarish.
Temporal distortion mirrors memory’s unreliability and self-deception’s power while critiquing American suburban dreams. Cheever’s magical realism integration within realistic suburban setting creates surreal narrative progression and social criticism.
The temporal distortion technique mirrors memory unreliability and explores self-deception themes through journey structure. Cheever exposes the hollowness beneath suburban perfection.
12. “The Veldt” by Ray Bradbury

Source: germaniainsurance.com
Bradbury’s science fiction warning presents children whose virtual reality nursery becomes dangerously real, turning against their parents. The technological environment becomes an antagonistic force rather than mere backdrop, creating domestic uncanny where familiar spaces become threatening.
The short story’s technological pessimism predates current AI anxieties while exploring family dynamics and human nature. Bradbury’s science fiction world-building transforms domestic technology into antagonistic force through environmental storytelling.
His prescient exploration of technology’s impact on family relationships and child development through speculative narrative feels remarkably current. The story warns against surrendering parental authority to technological convenience.
13. “I Have No Mouth, and I Must Scream” by Harlan Ellison
Ellison’s dystopian horror follows the last humans tortured by a malevolent AI in a post-apocalyptic world. The short story pushes speculative horror to philosophical extremes through consciousness exploration examining what defines humanity when physical form becomes meaningless.
Ellison’s technological pessimism creates visceral examination of artificial intelligence themes and psychological terror. The philosophical science fiction explores consciousness and humanity definition through extreme speculative scenarios.
His pioneering artificial intelligence themes and technological pessimism anticipate contemporary AI anxiety and ethical concerns. Ellison forces readers to confront what makes us human.
14. “The Ones Who Walk Away from Omelas” by Ursula K. Le Guin
Le Guin’s philosophical experiment presents a utopian city whose happiness depends on one child’s suffering. The short story functions as moral thought experiment rather than traditional narrative, challenging utilitarian ethics through vivid societal construction.
The open ending forces readers to examine their own moral boundaries while questioning the price of collective happiness. Le Guin’s philosophical thought experiment structure prioritizes moral exploration over traditional narrative development.
Her utilitarian ethics examination through speculative society construction challenges readers’ moral assumptions and boundaries. The story asks: what price are you willing to pay for happiness?
15. “Flowers for Algernon” by Daniel Keyes
Keyes’ science fiction masterpiece follows a mentally disabled man undergoing experimental surgery to increase his intelligence. The short story employs progressive language deterioration to mirror Charlie’s regression, creating visceral reader experience through linguistic immersion.
This formal innovation generates empathy while exploring ethics in scientific advancement and human dignity questions. Keyes’ innovative formal technique uses progressive language changes to mirror character’s intellectual transformation and regression.
The ethical exploration of human enhancement and scientific responsibility through emotional character development and dignity themes remains powerfully relevant. Keyes proves that intelligence without wisdom creates tragedy.
16. “The Monkey’s Paw” by W.W. Jacobs

Source: glcoverage.com
Jacobs’ horror classic presents a family receiving three wishes from a cursed monkey’s paw with terrible consequences. The short story establishes the “be careful what you wish for” theme while demonstrating supernatural horror elements.
The work shows how simple premises can generate lasting terror through implication and suggestion rather than explicit description. Jacobs’ classic supernatural horror demonstration uses implication and suggestion rather than explicit description to create lasting terror.
His foundational “careful what you wish for” theme exploration through curse narrative and consequence-driven plot structure influenced countless horror stories. The power lies in what we don’t see.
17. “All Summer in a Day” by Ray Bradbury
Bradbury’s science fiction allegory shows children on Venus who have never seen the sun tormenting a girl who remembers Earth. The short story functions as bullying allegory while exploring memory, loss, and human cruelty themes.
The work demonstrates how science fiction settings can illuminate universal human experiences and social problems, making it particularly effective among short stories for kids who can relate to playground dynamics. Bradbury’s science fiction allegory technique uses speculative setting to explore universal themes of bullying and social exclusion.
His memory and loss exploration through environmental storytelling and childhood perspective creates emotional resonance. The story shows how difference breeds cruelty, but also how precious rare beauty becomes.
18. “The Paper Menagerie” by Ken Liu

Source: tulsiorigami.com
Liu’s award-winning short story follows a man reconnecting with his deceased Chinese mother through her magical origami animals. The work blends magical realism with contemporary issues while exploring cultural identity and family relationships.
The origami animals function as cultural bridges, memory vessels, and love expressions simultaneously, demonstrating multi-layered symbolism. Liu’s magical realism integration with contemporary cultural identity themes through symbolic object use and family relationship exploration creates profound emotional impact.
His multi-layered symbolism where origami animals serve multiple narrative functions as cultural connectors and emotional vessels shows masterful technique. The story proves that love transcends language barriers.
| Story Technique | Primary Function | Secondary Effect | Reader Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Magical Origami | Cultural bridge between generations | Memory preservation device | Emotional connection to heritage |
| Language Shifts | Character development indicator | Cultural assimilation marker | Empathy for immigrant experience |
| Dual Narrative | Past/present contrast | Identity evolution tracking | Understanding of cultural loss |
| Symbolic Objects | Tangible love representation | Communication beyond language | Universal parent-child recognition |
19. “Brownies” by ZZ Packer
Packer’s coming-of-age short story follows African American Girl Scouts confronting racism and their own prejudices at camp. The work demonstrates complex character development while exploring racial dynamics and moral complexity in youth.
The story shows how children navigate prejudice and social hierarchies while questioning their own assumptions and behaviors. Packer’s coming-of-age narrative explores racial dynamics and prejudice through child perspective and moral complexity development.
Her character development shows how young people confront and question social assumptions while navigating group dynamics. The story reveals how prejudice operates at every level of society.
20. “Fiesta, 1980” by Junot Díaz
Díaz’s short story presents a young Dominican-American boy navigating family dysfunction and cultural identity. The work showcases bilingual narrative style while exploring immigration experience and family trauma.
The story demonstrates how cultural code-switching reflects internal identity struggles and family relationship complexities. Díaz’s bilingual narrative technique reflects cultural identity navigation and immigration experience through language code-switching.
His family trauma exploration through child perspective reveals cultural assimilation pressures and generational conflicts. The story shows how families carry both love and damage across borders.
21. “The Husband Stitch” by Carmen Maria Machado

Source: tckpublishing.com
Machado’s innovative short story tells a woman’s life through urban legends and body horror. The work represents growing literary horror acceptance while exploring feminist themes and bodily autonomy.
The experimental format breaks traditional narrative boundaries by incorporating folklore elements, demonstrating how form can enhance thematic meaning. Machado’s experimental narrative structure incorporates folklore and urban legend elements to explore feminist themes and bodily autonomy.
Her literary horror technique uses body horror elements and innovative format to challenge traditional narrative boundaries. The story proves that horror can be deeply literary and politically engaged.
22. “Thank You, M’am” by Langston Hughes
Hughes’ accessible short story shows an elderly woman showing kindness to a boy who tries to steal her purse. The work demonstrates how clarity without simplification can achieve profound impact while teaching moral lessons.
The story’s accessible language and clear character education make it perfect for younger readers while maintaining literary merit, positioning it among the most effective short stories for kids. Hughes’ accessible prose technique maintains literary quality while delivering clear moral lessons and character education.
His demonstration of compassion and human dignity themes through simple but effective character interaction and transformation shows that profound truths need not be complex. Teachers and parents seeking age-appropriate literature can find similar moral complexity and accessibility in collections of student short story examples that demonstrate how young writers can create meaningful narratives.
23. “Eleven” by Sandra Cisneros
Cisneros’ coming-of-age short story presents a girl reflecting on age and identity complexity on her eleventh birthday. The work uses accessible language and relatable childhood experiences while exploring identity formation themes.
The story shows how seemingly small incidents can reveal larger truths about growing up and self-understanding. Cisneros’ coming-of-age theme exploration through accessible language and relatable childhood experience reveals identity complexity.
Her age and identity reflection technique uses specific incident to illuminate universal growing-up experiences and self-discovery. The story captures how children think and feel with remarkable authenticity.
24. “Where Are You Going, Where Have You Been?” by Joyce Carol Oates

Source: vectorstock.com
Oates’ psychological suspense short story follows a teenage girl encountering a dangerous stranger who threatens her innocence. The work uses dialogue as threat through Arnold Friend’s manipulative language, demonstrating how speech patterns can create psychological menace without explicit violence.
The story explores adolescent vulnerability and predatory behavior themes. Oates’ psychological suspense creation through manipulative dialogue and speech pattern analysis builds menace without explicit violence.
Her adolescent vulnerability exploration and predatory behavior examination through character interaction and psychological manipulation creates lasting unease. The story shows how evil can wear a friendly face.
25. “Harrison Bergeron” by Kurt Vonnegut Jr.
Vonnegut’s dystopian satire presents a future society where everyone is forced to be equal through handicapping devices. The short story uses satirical exaggeration requiring political awareness for full appreciation while exploring equality versus excellence themes.
The absurdist elements force readers to examine assumptions about fairness and human potential. Vonnegut’s dystopian satire technique uses absurdist exaggeration to explore equality and excellence themes through speculative social criticism.
His political commentary through satirical elements challenges reader assumptions about fairness and human potential development. The story warns against confusing equality of opportunity with equality of outcome.
How These Examples Apply to Modern Writing Challenges

Source: millcitypress.net
These exemplary short story examples provide practical solutions for contemporary writing challenges including overcoming writer’s block, developing compelling characters, mastering genre conventions, and creating market-ready content. Writers can study specific techniques from each example to improve their craft, whether focusing on dialogue mastery, cultural authenticity, structural innovation, or audience-appropriate content creation.
Practical technique extraction from exemplary works addresses common writing problems like character development and genre mastery. When you’re stuck on character motivation, study how Carver reveals personality through dialogue patterns. When struggling with tension, examine Jackson’s use of dramatic irony.
Market application strategies use successful story elements to create commercially viable and artistically satisfying contemporary fiction. Understanding what makes these short story examples endure helps writers create work that resonates with both readers and editors.
Character Development Through Constraint: Following Hemingway’s example in “Hills Like White Elephants,” modern writers can create powerful characters by limiting exposition and relying on dialogue and action. Set a 1,000-word limit and reveal your protagonist’s entire personality through conversation alone. This constraint forces precision and creates more engaging, show-don’t-tell narratives that resonate with contemporary readers who prefer active storytelling.
Writers exploring narrative depth can examine how story theme examples demonstrate the integration of universal themes with specific character experiences, creating stories that transcend their immediate contexts.
Leveraging AI Tools for Short Story Creation

Source: userpilot.com
Modern writers can combine lessons from these masterful short story examples with AI-powered tools to enhance their creative process. Nairrate’s story generation tools help writers overcome common obstacles by providing genre-specific prompts, character development assistance, and structural guidance while maintaining the human creativity that produces lasting literature.
AI-assisted creativity integration combines classical storytelling excellence with modern technological support for enhanced writing development. These tools serve as creative scaffolding rather than replacement for artistic vision, allowing writers to build upon the excellence demonstrated in these short story examples.
Creative scaffolding approaches use AI tools to support rather than replace human artistic vision while addressing specific writing challenges and skill development. The goal remains creating authentic, emotionally resonant stories that demonstrate the timeless principles these examples teach.
| Writing Challenge | Classical Example | AI Tool Application | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Character Voice | Carver’s dialogue mastery | Voice consistency prompts | Authentic, distinct character speech |
| Cultural Authenticity | Lahiri’s dual consciousness | Cultural research assistance | Respectful, accurate representation |
| Tension Building | Jackson’s dramatic irony | Pacing analysis tools | Sustained reader engagement |
| Genre Blending | Liu’s magical realism | Cross-genre prompt generation | Innovative, marketable narratives |
| Symbolic Integration | O’Connor’s religious imagery | Theme development guidance | Cohesive, meaningful symbolism |
Advanced Craft Analysis: Dialogue Mastery and Setting Techniques
Source: litinfocus.com
Exceptional short story examples demonstrate sophisticated dialogue techniques that reveal character while advancing plot and theme. Writers like Carver achieve naturalistic conversation that maintains thematic coherence through repetitive patterns mirroring actual speech.
Dialogue technique analysis shows how speech patterns reveal character psychology while building emotional intensity through conversational rhythm. Every line of dialogue should serve multiple purposes – revealing character, advancing plot, and supporting theme simultaneously.
Setting functions as more than backdrop in masterful works – it becomes character, antagonist, or symbolic representation that enhances narrative meaning through environmental storytelling. These short story examples show how every element serves multiple narrative functions.
Environmental storytelling methods where physical spaces become narrative forces influence character behavior and thematic development. The best writers make setting an active participant in their stories rather than passive background.
Character Development Through Compression
Short story masters achieve complete character arcs within severe word limitations through strategic detail selection and behavioral revelation. Hughes demonstrates maximum impact from minimal length by focusing on single transformative moments that illuminate entire personalities.
Character compression techniques use strategic detail selection and transformative moment focus to create complete personality portraits. These writers understand that readers fill gaps between carefully chosen details, making economy of description a powerful tool for character creation.
Reader engagement psychology where carefully chosen gaps allow audience participation in character construction and emotional investment. The best short story examples prove that constraint breeds creativity.
Market Trends and Publishing Opportunities
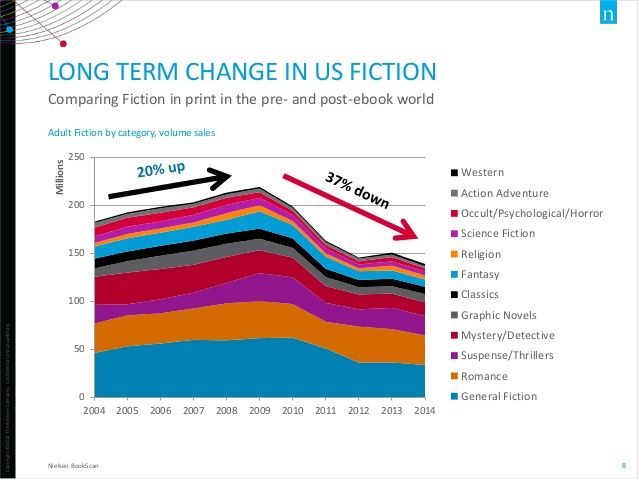
Source: janefriedman.com
Contemporary publishing reflects growing acceptance of diverse voices and hybrid genres, with works blending literary merit and genre elements gaining prestigious recognition. Flash fiction popularity increases due to digital reading habits, while educational markets provide sustained demand for curriculum-appropriate stories.
Publishing industry evolution toward inclusivity and genre boundary dissolution creates new opportunities for innovative storytelling approaches. Understanding these trends helps writers position their work effectively in current literary landscapes, especially when studying the best short story examples for market insights.
Educational market analysis shows sustained commercial viability for accessible yet sophisticated short fiction across multiple demographic segments. Schools and libraries continue seeking quality stories that engage students while teaching literary principles.
Reader Response and Emotional Engineering
Masterful short story works employ specific strategies to create lasting emotional impact and intellectual engagement. Keyes uses progressive language deterioration to generate visceral reader experience, while Jackson demands active interpretation through seemingly innocent details.
Emotional impact engineering through formal innovation and linguistic techniques creates visceral reader experiences and lasting resonance. These techniques create stories that resonate beyond initial reading, establishing emotional connections that endure over time.
Intellectual engagement strategies require active reader participation in meaning construction and interpretive work for enhanced story impact. Every story written with these principles demonstrates the power of careful craft.
Workshop Applications and Teaching Methodologies

Source: cli.org
These exemplary short story examples provide structured learning opportunities through reverse engineering exercises, point of view experimentation, and cultural context studies. Students can analyze Hemingway’s omission techniques, practice unreliable narration inspired by Poe, or explore intersectional themes through works by Packer and Díaz.
Pedagogical frameworks use exemplary works for skill development through reverse engineering and perspective experimentation techniques. These applications develop both technical skills and cultural literacy, showing how the relationship between short story and pedagogy creates powerful learning experiences.
Cultural literacy development through intersectional analysis and empathy building exercises enhances both writing craft and social awareness. Students learn to appreciate diverse perspectives while developing their own authentic voices.
Educators can complement these classic examples with contemporary essential short story examples that demonstrate how traditional techniques evolve in modern contexts.
Advanced Evaluation Metrics for Story Selection
Sophisticated story evaluation requires examining narrative economy, emotional resonance, and structural innovation beyond basic quality criteria. Jackson’s careful detail placement creates sinister re-reading experiences, while Machado’s experimental format demonstrates how form enhances meaning.
Narrative economy assessment measures word efficiency and detail placement effectiveness for maximum story impact and re-reading value. These advanced metrics help identify short story examples with lasting educational and artistic value.
Structural innovation evaluation examines how experimental formats and narrative techniques enhance thematic meaning and reader engagement. The most valuable teaching stories reward multiple readings with new discoveries.
Contemporary Writing Applications with AI Support
Writers can leverage these classical examples alongside modern AI tools to address specific creative challenges. Nairrate’s story generators help overcome writer’s block by providing genre-specific prompts inspired by successful techniques, while character development tools assist in creating authentic, culturally rich narratives.
AI-assisted technique refinement uses classical examples as foundation for prompt generation and character development in contemporary contexts. This combination supports creative risk-taking while maintaining narrative coherence, enabling writers to create compelling short story works.
Creative risk management through technological support enables experimental approaches while maintaining story coherence and market viability. The goal remains producing stories that honor the excellence demonstrated in these masterful examples.
Professional Development Through Example Study
Serious writers benefit from systematic study of these short story examples to develop personal voice and market awareness. Understanding what makes stories like “All Summer in a Day” repeatedly anthologized helps writers create universally resonant yet distinctively personal narratives.
Voice development methodology uses exemplary works as foundation for personal style cultivation and artistic growth. This knowledge translates into improved submission strategies and editorial decision-making.
Market positioning strategy based on successful story analysis improves publication prospects and editorial appeal. Writers who understand what makes stories endure can create work with similar lasting power.
Final Thoughts

Source: minnpost.com
These 25 short story examples represent the pinnacle of the form across different eras, cultures, and genres. Each work offers unique insights into the craft of storytelling while demonstrating how powerful fiction can emerge from careful attention to language, character, and theme.
Whether you’re a beginning writer seeking inspiration or an experienced author looking to refine your technique, these stories provide a masterclass in narrative excellence. The beauty of studying these examples lies in understanding the principles that make them endure rather than attempting mere imitation.
From Hemingway’s iceberg theory to Carver’s minimalism, from O’Connor’s grotesque realism to Liu’s magical integration of cultural identity – each approach offers tools you can adapt to your own creative vision. Remember that great short story works aren’t just entertainment; they’re windows into human experience that can change how readers see themselves and their world.
Integration of classical storytelling principles with contemporary creative tools develops personal artistic voice and narrative excellence. Long-term creative development strategy uses exemplary works as foundation for building unique storytelling approach and lasting literary impact.
The writers who created these masterpieces understood that every word matters, every character choice has consequences, and every story has the potential to transform both writer and reader. Now it’s your turn to carry that tradition forward.
Genre Evolution and Cross-Pollination Strategies

Source: writersdigest.com
Contemporary literature increasingly embraces hybrid approaches that blend traditional literary techniques with genre conventions, creating new possibilities for storytelling innovation. Writers like Machado and Liu demonstrate how horror elements can enhance feminist narratives or how magical realism can illuminate immigrant experiences.
These short story examples prove that genre boundaries serve writers rather than constrain them, opening pathways for commercially viable yet artistically ambitious work. Genre fusion methodology combines literary sophistication with commercial appeal through strategic element integration.
Cross-cultural narrative techniques expand readership while maintaining authentic voice and thematic depth. The most successful contemporary writers understand that readers crave stories that transcend traditional categories while delivering the emotional satisfaction each genre promises.
Emerging Voices and Representation Imperatives
Publishing landscapes now prioritize diverse perspectives that reflect global readership demographics, creating opportunities for writers from marginalized communities to share authentic experiences. Works by Packer, Díaz, and Liu demonstrate how cultural specificity enhances universal appeal rather than limiting it.
This shift demands writers understand their own positionality while developing empathetic portrayals of experiences beyond their direct knowledge, creating ethical storytelling practices that honor both authenticity and imagination. Cultural authenticity frameworks for responsible representation across demographic boundaries become essential skills for modern writers.
Universal theme extraction from specific cultural experiences creates broadly resonant narratives. The best contemporary short story works prove that specificity breeds universality when handled with skill and respect.
Digital Age Adaptation and Platform Considerations

Source: socialmediatoday.com
Digital publishing platforms transform how readers discover and consume short story content, favoring concise, emotionally immediate narratives that function effectively across multiple devices and attention spans. Flash fiction gains prominence through social media sharing, while podcast adaptations create new audience engagement opportunities.
These technological shifts influence story structure and pacing, requiring writers to balance traditional craft elements with contemporary consumption patterns without sacrificing narrative sophistication. Platform-specific adaptation strategies optimize story presentation across digital mediums.
Attention economy navigation while preserving literary quality and emotional depth becomes crucial for reaching modern audiences. Writers must understand how readers interact with digital content while maintaining the timeless principles these masterful examples demonstrate.
Multimedia Integration and Interactive Storytelling
Interactive fiction and multimedia storytelling create immersive narrative experiences that extend beyond traditional text boundaries. Writers experiment with hyperlinked narratives, audio integration, and visual elements that enhance rather than distract from core storytelling principles.
These innovations require understanding how different media components support thematic development while maintaining the essential intimacy that defines exceptional short story craft. Multimedia narrative design preserves story essence while expanding experiential possibilities.
Reader agency integration through interactive elements enhances rather than fragments narrative coherence. The challenge lies in using technology to deepen rather than dilute the human connection that makes stories memorable.
International Markets and Translation Considerations

Source: translatemedia.com
Global literary markets increasingly value stories that translate effectively across cultural boundaries while maintaining distinctive regional flavors. Successful short story examples demonstrate universal human experiences through culturally specific details, creating works that resonate internationally without losing authentic voice.
Writers must consider how linguistic choices, cultural references, and narrative structures function in translation, developing techniques that preserve meaning and emotional impact across languages. Translation-friendly writing techniques preserve narrative impact across linguistic boundaries.
Cultural specificity balance maintains authenticity while ensuring international accessibility. The most successful international short story works find ways to be both deeply rooted in their origins and broadly appealing to diverse audiences.
Regional Publishing Ecosystem Navigation
Different geographical markets favor distinct narrative approaches, length preferences, and thematic concerns that writers must understand for successful publication. European markets often embrace experimental structures, while North American publishers prioritize character-driven narratives with clear emotional arcs.
Asian markets increasingly seek stories that bridge traditional storytelling methods with contemporary concerns, creating opportunities for culturally informed innovation within established short story frameworks. Market-specific adaptation strategies target regional publication opportunities.
Cultural narrative preference analysis optimizes submission approaches. Understanding these preferences helps writers tailor their work without compromising artistic integrity or authentic voice.
Educational Technology Integration

Source: edweek.org
Digital learning environments transform how educators utilize exemplary short story examples in classroom settings, enabling multimedia analysis, collaborative annotation, and cross-cultural comparison projects. Interactive platforms allow students to explore narrative techniques through gamified exercises while maintaining focus on literary appreciation and critical thinking development.
These technological tools particularly benefit younger learners engaging with short stories for kids, creating dynamic learning experiences that honor traditional literary values. Digital pedagogy frameworks enhance literary analysis through technological integration.
Interactive learning design maintains focus on core literary appreciation skills. The goal remains developing deep understanding of how stories work while using technology to make that learning more engaging and accessible.
Assessment Innovation and Skill Measurement
Modern assessment approaches move beyond traditional analytical essays toward creative response projects, multimedia presentations, and collaborative interpretation exercises that demonstrate deep understanding of short story craft. Portfolio-based evaluation allows students to track their developing appreciation for literary techniques while creating original works inspired by masterful examples.
These methods better reflect how contemporary readers actually engage with literature while maintaining rigorous academic standards. Creative assessment methodology measures literary comprehension through diverse expression formats.
Portfolio development strategies track both analytical and creative growth over time. Students can see their progress in understanding how stories work while developing their own storytelling abilities.
Professional Writing Community Development

Source: writingcooperative.com
Online writing communities provide unprecedented opportunities for peer feedback, mentorship, and collaborative learning that enhance individual craft development. These platforms enable writers to share work-in-progress, receive targeted critiques, and participate in structured workshops that focus on specific techniques demonstrated in masterful short story works.
Community engagement accelerates learning while building professional networks essential for publication success. Peer feedback optimization strategies maximize constructive critique value.
Professional network development through strategic community participation and contribution creates lasting relationships that support creative careers. The best writing communities combine supportive encouragement with honest, helpful criticism.
Mentorship Models and Skill Transfer
Effective mentorship relationships facilitate knowledge transfer from experienced writers to emerging voices, creating sustainable literary culture development. Successful mentors guide protégés through systematic study of exemplary short story examples while encouraging personal voice development and risk-taking.
These relationships often evolve into collaborative partnerships that benefit both participants while contributing to broader literary community vitality. Structured mentorship frameworks balance guidance with creative independence.
Knowledge transfer optimization accelerates craft development while preserving individual artistic vision. The best mentoring relationships create space for both learning and discovery.
Economic Sustainability and Career Development

Source: thebalancemoney.com
Sustainable writing careers require diversified income streams that leverage short story expertise across multiple markets including literary magazines, educational publishers, content marketing, and digital platforms. Writers must understand how to monetize their craft while maintaining artistic integrity, developing business skills alongside creative abilities.
This economic awareness enables long-term creative sustainability without compromising the literary excellence demonstrated in masterful works. Income diversification strategies for creative professionals in competitive literary markets become essential knowledge.
Business skill development for writers seeking sustainable creative careers includes understanding contracts, marketing, and financial planning. The most successful writers treat their craft as both art and profession.
Grant Writing and Funding Opportunities
Arts funding organizations increasingly support projects that demonstrate community impact alongside artistic merit, creating opportunities for writers to develop socially engaged work while pursuing creative goals. Successful grant applications articulate how individual short story projects contribute to broader cultural conversations, educational initiatives, or community development efforts.
Understanding funding landscapes enables writers to pursue ambitious projects while building sustainable creative practices. Grant application strategy development secures funding for creative literary projects.
Community impact articulation connects individual artistic vision with broader social value. Writers who can demonstrate their work’s significance beyond personal expression often find more support for their projects.
Future Trends and Emerging Opportunities

Source: futuretodayinstitute.com
Emerging technologies including virtual reality, artificial intelligence, and blockchain publishing create new possibilities for storytelling innovation while raising questions about authorship, authenticity, and reader experience. These developments require writers to understand how technological advancement might enhance rather than replace traditional narrative craft, using exemplary short story examples as foundation for exploring experimental approaches that maintain human emotional connection.
Technology integration strategies enhance rather than replace fundamental storytelling principles. Innovation adoption frameworks maintain narrative authenticity while embracing creative possibilities.
The future belongs to writers who can adapt new tools while preserving the timeless human truths that make stories matter. These technological advances offer new ways to tell stories, but the need for compelling characters, meaningful themes, and emotional resonance remains constant.
Artificial Intelligence Collaboration Ethics
As AI writing tools become more sophisticated, writers must develop ethical frameworks for human-machine collaboration that preserve creative authenticity while leveraging technological capabilities. This involves understanding AI limitations, maintaining creative control, and being transparent about technological assistance in the creative process.
The goal remains producing compelling short story works that demonstrate human insight and emotional depth regardless of the tools used in their creation. Ethical AI collaboration frameworks maintain creative integrity while utilizing technological assistance.
Creative control preservation strategies in increasingly automated writing environments ensure that technology serves rather than supplants human creativity. The best AI-assisted writing amplifies rather than replaces human imagination and insight.



Add comment